Page 35 - FPGEE Medicinal and Organic Chemistry Q&A Book
P. 35
Krisman
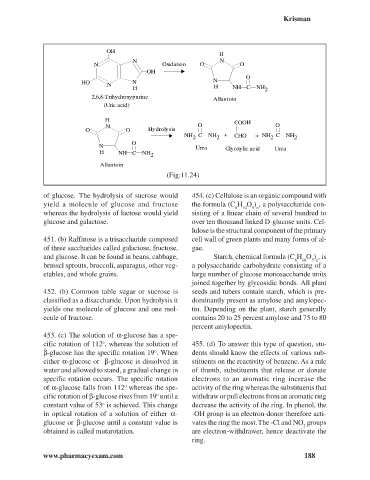
OH
H
N N
N Oxidation O O
OH
O
H O N N
N H
H NH C NH 2
2,6,8-Trihydroxypurine Allantoin
(Uric acid)
H COOH
N O O
O O Hydrolysis
NH C NH + CHO + NH C NH
2 2 2 2
O
N Urea Glyoxylic acid Urea
H NH C NH
2
Allantoin
(Fig:11.24)
of glucose. The hydrolysis of sucrose would 454. (c) Cellulose is an organic compound with
yield a molecule of glucose and fructose the formula (C H O ) , a polysaccharide con-
6 10 5 n
whereas the hydrolysis of lactose would yield sisting of a linear chain of several hundred to
glucose and galactose. over ten thousand linked D-glucose units. Cel-
lulose is the structural component of the primary
451. (b) Raffinose is a trisaccharide composed cell wall of green plants and many forms of al-
of three saccharides called galactose, fructose, gae.
and glucose. It can be found in beans, cabbage, Starch, chemical formula (C H O ) , is
6 10 5 n
brussel sprouts, broccoli, asparagus, other veg- a polysaccharide carbohydrate consisting of a
etables, and whole grains. large number of glucose monosaccharide units
joined together by glycosidic bonds. All plant
452. (b) Common table sugar or sucrose is seeds and tubers contain starch, which is pre-
classified as a disaccharide. Upon hydrolysis it dominantly present as amylose and amylopec-
yields one molecule of glucose and one mol- tin. Depending on the plant, starch generally
ecule of fructose. contains 20 to 25 percent amylose and 75 to 80
percent amylopectin.
453. (c) The solution of a-glucose has a spe-
o
cific rotation of 112 , whereas the solution of 455. (d) To answer this type of question, stu-
o
b-glucose has the specific rotation 19 . When dents should know the effects of various sub-
either a-glucose or b-glucose is dissolved in stituents on the reactivity of benzene. As a rule
water and allowed to stand, a gradual change in of thumb, substituents that release or donate
specific rotation occurs. The specific rotation electrons to an aromatic ring increase the
o
of a-glucose falls from 112 whereas the spe- activity of the ring whereas the substituents that
cific rotation of b-glucose rises from 19 until a withdraw or pull electrons from an aromatic ring
o
o
constant value of 53 is achieved. This change decrease the activity of the ring. In phenol, the
in optical rotation of a solution of either a- -OH group is an electron-donor therefore acti-
glucose or b-glucose until a constant value is vates the ring the most. The -Cl and NO groups
2
obtained is called mutarotation. are electron-withdrawer, hence deactivate the
ring.
www.pharmacyexam.com 188