Page 32 - FPGEE Medicinal and Organic Chemistry Q&A Book
P. 32
Krisman
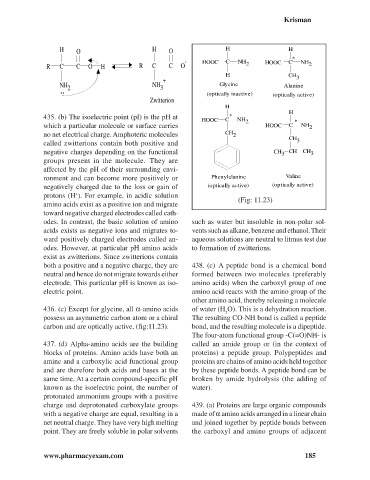
H O H O H H
*
- HOOC C NH HOOC C NH
R C C O H R C C O 2 2
H CH
+ 3
NH NH Glycine Alanine
.. 2 3
(optically inactive) (optically active)
Zwitterion
H
H
435. (b) The isoelectric point (pI) is the pH at *
HOOC C NH 2 *
which a particular molecule or surface carries HOOC C NH 2
no net electrical charge. Amphoteric molecules CH 2
CH
called zwitterions contain both positive and 3
negative charges depending on the functional CH 3 CH CH 3
groups present in the molecule. They are
affected by the pH of their surrounding envi-
ronment and can become more positively or Phenylalanine Valine
negatively charged due to the loss or gain of (optically active) (optically active)
protons (H ). For example, in acidic solution
+
(Fig: 11.23)
amino acids exist as a positive ion and migrate
toward negative charged electrodes called cath-
odes. In contrast, the basic solution of amino such as water but insoluble in non-polar sol-
acids exists as negative ions and migrates to- vents such as alkane, benzene and ethanol. Their
ward positively charged electrodes called an- aqueous solutions are neutral to litmus test due
odes. However, at particular pH amino acids to formation of zwitterions.
exist as zwitterions. Since zwitterions contain
both a positive and a negative charge, they are 438. (c) A peptide bond is a chemical bond
neutral and hence do not migrate towards either formed between two molecules (preferably
electrode. This particular pH is known as iso- amino acids) when the carboxyl group of one
electric point. amino acid reacts with the amino group of the
other amino acid, thereby releasing a molecule
436. (c) Except for glycine, all a-amino acids of water (H O). This is a dehydration reaction.
2
possess an asymmetric carbon atom or a chiral The resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide
carbon and are optically active, (fig:11.23). bond, and the resulting molecule is a dipeptide.
The four-atom functional group -C(=O)NH- is
437. (d) Alpha-amino acids are the building called an amide group or (in the context of
blocks of proteins. Amino acids have both an proteins) a peptide group. Polypeptides and
amine and a carboxylic acid functional group proteins are chains of amino acids held together
and are therefore both acids and bases at the by these peptide bonds. A peptide bond can be
same time. At a certain compound-specific pH broken by amide hydrolysis (the adding of
known as the isoelectric point, the number of water).
protonated ammonium groups with a positive
charge and deprotonated carboxylate groups 439. (a) Proteins are large organic compounds
with a negative charge are equal, resulting in a made of a amino acids arranged in a linear chain
net neutral charge. They have very high melting and joined together by peptide bonds between
point. They are freely soluble in polar solvents the carboxyl and amino groups of adjacent
www.pharmacyexam.com 185