Page 34 - FPGEE Medicinal and Organic Chemistry Q&A Book
P. 34
Krisman
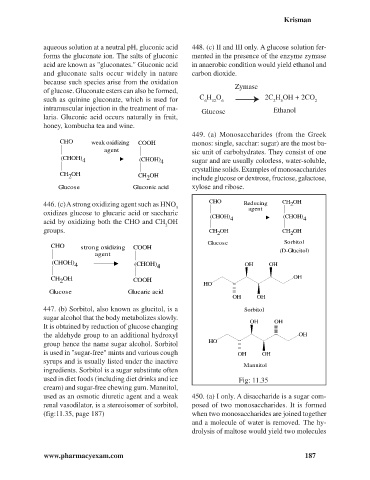
aqueous solution at a neutral pH, gluconic acid 448. (c) II and III only. A glucose solution fer-
forms the gluconate ion. The salts of gluconic mented in the presence of the enzyme zymase
acid are known as "gluconates." Gluconic acid in anaerobic condition would yield ethanol and
and gluconate salts occur widely in nature carbon dioxide.
because such species arise from the oxidation
Zymase
of glucose. Gluconate esters can also be formed,
such as quinine gluconate, which is used for C H O 6 2C H OH + 2CO 2
5
2
12
6
intramuscular injection in the treatment of ma- Ethanol
Glucose
laria. Gluconic acid occurs naturally in fruit,
honey, kombucha tea and wine.
449. (a) Monosaccharides (from the Greek
CHO weak oxidizing COOH monos: single, sacchar: sugar) are the most ba-
agent sic unit of carbohydrates. They consist of one
(CHOH) (CHOH)
4 4 sugar and are usually colorless, water-soluble,
crystalline solids. Examples of monosaccharides
CH OH
2 CH OH include glucose or dextrose, fructose, galactose,
2
Glucose Gluconic acid xylose and ribose.
CHO CH OH
446. (c) A strong oxidizing agent such as HNO Reducing 2
3 agent
oxidizes glucose to glucaric acid or saccharic
(CHOH) (CHOH)
acid by oxidizing both the CHO and CH OH 4 4
2
groups. CH OH CH OH
2 2
Glucose Sorbitol
CHO strong oxidizing COOH
agent (D-Glucitol)
(CHOH)
4 (CHOH) 4 OH OH
CH OH COOH OH
2
H O
Glucose Glucaric acid
OH OH
447. (b) Sorbitol, also known as glucitol, is a Sorbitol
sugar alcohol that the body metabolizes slowly.
OH OH
It is obtained by reduction of glucose changing
the aldehyde group to an additional hydroxyl OH
group hence the name sugar alcohol. Sorbitol H O
is used in "sugar-free" mints and various cough OH OH
syrups and is usually listed under the inactive
Mannitol
ingredients. Sorbitol is a sugar substitute often
used in diet foods (including diet drinks and ice Fig: 11.35
cream) and sugar-free chewing gum. Mannitol,
used as an osmotic diuretic agent and a weak 450. (a) I only. A disaccharide is a sugar com-
renal vasodilator, is a stereoisomer of sorbitol, posed of two monosaccharides. It is formed
(fig:11.35, page 187) when two monosaccharides are joined together
and a molecule of water is removed. The hy-
drolysis of maltose would yield two molecules
www.pharmacyexam.com 187