Page 43 - FPGEE Medicinal and Organic Chemistry Q&A Book
P. 43
Krisman
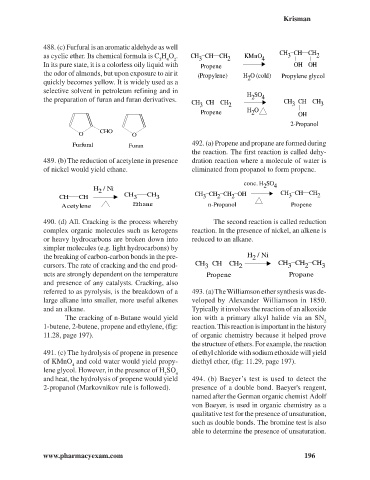
488. (c) Furfural is an aromatic aldehyde as well
CH CH CH
as cyclic ether. Its chemical formula is C H O . CH CH CH KMnO 3 2
5 4 2 3 2 4
In its pure state, it is a colorless oily liquid with Propene OH OH
the odor of almonds, but upon exposure to air it (Propylene) H O (cold) Propylene glycol
quickly becomes yellow. It is widely used as a 2
selective solvent in petroleum refining and in
H SO
the preparation of furan and furan derivatives. 2 4
CH CH CH CH 3 CH CH 3
3 2
Propene H O OH
2
2-Propanol
CHO
O O
Furfural Furan 492. (a) Propene and propane are formed during
the reaction. The first reaction is called dehy-
489. (b) The reduction of acetylene in presence dration reaction where a molecule of water is
of nickel would yield ethane. eliminated from propanol to form propene.
conc. H SO
H / Ni 2 4
2 CH CH CH
CH CH CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 OH 3 2
Acetylene Ethane n-Propanol Propene
490. (d) All. Cracking is the process whereby The second reaction is called reduction
complex organic molecules such as kerogens reaction. In the presence of nickel, an alkene is
or heavy hydrocarbons are broken down into reduced to an alkane.
simpler molecules (e.g. light hydrocarbons) by
the breaking of carbon-carbon bonds in the pre- H / Ni
2
cursors. The rate of cracking and the end prod- CH 3 CH CH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CH 3
ucts are strongly dependent on the temperature Propene Propane
and presence of any catalysts. Cracking, also
referred to as pyrolysis, is the breakdown of a 493. (a) The Williamson ether synthesis was de-
large alkane into smaller, more useful alkenes veloped by Alexander Williamson in 1850.
and an alkane. Typically it involves the reaction of an alkoxide
The cracking of n-Butane would yield ion with a primary alkyl halide via an SN
2
1-butene, 2-butene, propene and ethylene, (fig: reaction. This reaction is important in the history
11.28, page 197). of organic chemistry because it helped prove
the structure of ethers. For example, the reaction
491. (c) The hydrolysis of propene in presence of ethyl chloride with sodium ethoxide will yield
of KMnO and cold water would yield propy- diethyl ether, (fig: 11.29, page 197).
4
lene glycol. However, in the presence of H SO
2 4
and heat, the hydrolysis of propene would yield 494. (b) Baeyer’s test is used to detect the
2-propanol (Markovnikov rule is followed). presence of a double bond. Baeyer's reagent,
named after the German organic chemist Adolf
von Baeyer, is used in organic chemistry as a
qualitative test for the presence of unsaturation,
such as double bonds. The bromine test is also
able to determine the presence of unsaturation.
www.pharmacyexam.com 196