Page 42 - FPGEE Medicinal and Organic Chemistry Q&A Book
P. 42
Krisman
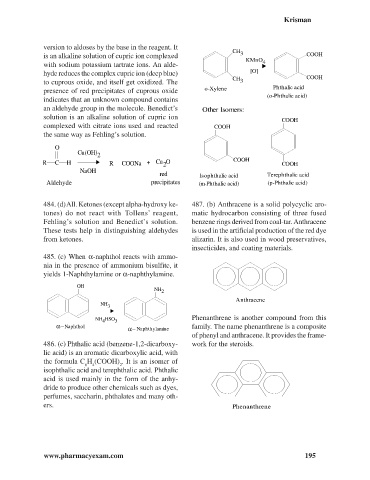
version to aldoses by the base in the reagent. It
CH
is an alkaline solution of cupric ion complexed 3 COOH
KMnO
with sodium potassium tartrate ions. An alde- 4
hyde reduces the complex cupric ion (deep blue) [O]
CH COOH
to cuprous oxide, and itself get oxidized. The 3
presence of red precipitates of cuprous oxide o-Xylene Phthalic acid
(o-Phthalic acid)
indicates that an unknown compound contains
an aldehyde group in the molecule. Benedict’s Other Isomers:
solution is an alkaline solution of cupric ion
COOH
complexed with citrate ions used and reacted COOH
the same way as Fehling’s solution.
O
Cu(OH)
2
R C H R COONa + Cu O COOH COOH
2
NaOH
red Isophthalic acid Terephthalic acid
Aldehyde precipitates (m-Phthalic acid) (p-Phthalic acid)
484. (d) All. Ketones (except alpha-hydroxy ke- 487. (b) Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aro-
tones) do not react with Tollens’ reagent, matic hydrocarbon consisting of three fused
Fehling’s solution and Benedict’s solution. benzene rings derived from coal-tar. Anthracene
These tests help in distinguishing aldehydes is used in the artificial production of the red dye
from ketones. alizarin. It is also used in wood preservatives,
insecticides, and coating materials.
485. (c) When a-naphthol reacts with ammo-
nia in the presence of ammonium bisulfite, it
yields 1-Naphthylamine or a-naphthylamine.
OH
NH
2
Anthracene
NH
3
NH HSO 3 Phenanthrene is another compound from this
4
a- Naphthol family. The name phenanthrene is a composite
a- Naphthylamine
of phenyl and anthracene. It provides the frame-
486. (c) Phthalic acid (benzene-1,2-dicarboxy- work for the steroids.
lic acid) is an aromatic dicarboxylic acid, with
the formula C H (COOH) . It is an isomer of
6 4 2
isophthalic acid and terephthalic acid. Phthalic
acid is used mainly in the form of the anhy-
dride to produce other chemicals such as dyes,
perfumes, saccharin, phthalates and many oth-
ers. Phenanthrene
www.pharmacyexam.com 195