Page 16 - Reference Guide For Foreign Pharmacy Licensing Exam Theory
P. 16
www.pharmacyexam.com Krisman
Polarity of molecules:
A molecule is considered to be a polar if the center of negative charge does not coincide with the center of
positive charge.
Molecules like H 2, N 2, O 2, Cl 2 and Br 2 have zero dipole moment and are considered to be nonpolar.
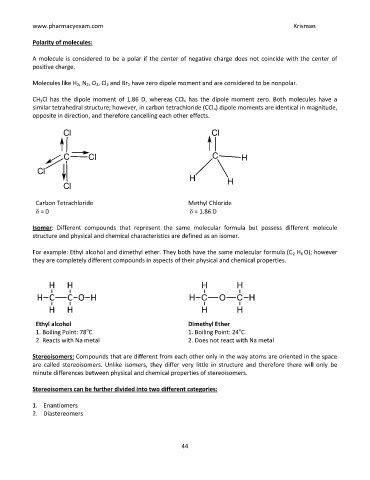
CH 3Cl has the dipole moment of 1.86 D, whereas CCl 4 has the dipole moment zero. Both molecules have a
similar tetrahedral structure; however, in carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4) dipole moments are identical in magnitude,
opposite in direction, and therefore cancelling each other effects.
Carbon Tetrachloride Methyl Chloride
= 0 = 1.86 D
Isomer: Different compounds that represent the same molecular formula but possess different molecule
structure and physical and chemical characteristics are defined as an isomer.
For example: Ethyl alcohol and dimethyl ether. They both have the same molecular formula (C 2 H 6 O); however
they are completely different compounds in aspects of their physical and chemical properties.
Ethyl alcohol Dimethyl Ether
o
o
1. Boiling Point: 78 C 1. Boiling Point: 24 C
2. Reacts with Na metal 2. Does not react with Na metal
Stereoisomers: Compounds that are different from each other only in the way atoms are oriented in the space
are called stereoisomers. Unlike isomers, they differ very little in structure and therefore there will only be
minute differences between physical and chemical properties of stereoisomers.
Stereoisomers can be further divided into two different categories:
1. Enantiomers
2. Diastereomers
44