Page 7 - Referance Guide For Pharmaceutical Calculations (Naplex, Fpgee and Ptce)
P. 7
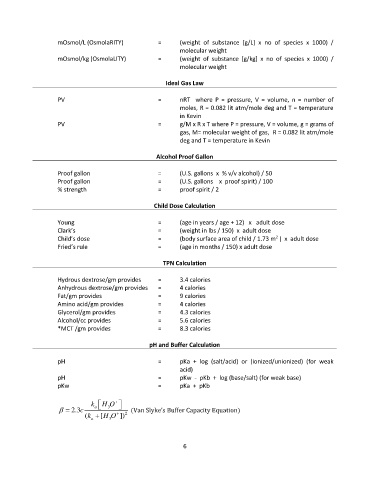
mOsmol/L (OsmolaRITY) = (weight of substance [g/L] x no of species x 1000) /
molecular weight
mOsmol/kg (OsmolaLITY) = (weight of substance [g/kg] x no of species x 1000) /
molecular weight
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT where P = pressure, V = volume, n = number of
moles, R = 0.082 lit atm/mole deg and T = temperature
in Kevin
PV = g/M x R x T where P = pressure, V = volume, g = grams of
gas, M= molecular weight of gas, R = 0.082 lit atm/mole
deg and T = temperature in Kevin
Alcohol Proof Gallon
Proof gallon = (U.S. gallons x % v/v alcohol) / 50
Proof gallon = (U.S. gallons x proof spirit) / 100
% strength = proof spirit / 2
Child Dose Calculation
Young = (age in years / age + 12) x adult dose
Clark’s = (weight in lbs / 150) x adult dose
2
Child’s dose = (body surface area of child / 1.73 m ) x adult dose
Fried’s rule = (age in months / 150) x adult dose
TPN Calculation
Hydrous dextrose/gm provides = 3.4 calories
Anhydrous dextrose/gm provides = 4 calories
Fat/gm provides = 9 calories
Amino acid/gm provides = 4 calories
Glycerol/gm provides = 4.3 calories
Alcohol/cc provides = 5.6 calories
*MCT /gm provides = 8.3 calories
pH and Buffer Calculation
pH = pKa + log (salt/acid) or (ionized/unionized) (for weak
acid)
pH = pKw - pKb + log (base/salt) (for weak base)
pKw = pKa + pKb
k H O +
= 2.3c a 3 (Van Slyke’s Buffer Capacity Equation)
(k + [H O + ]) 2
a
3
6