Page 14 - Pharmacy College Admission Test Review Book
P. 14
www.pharmacyexam.com Krisman
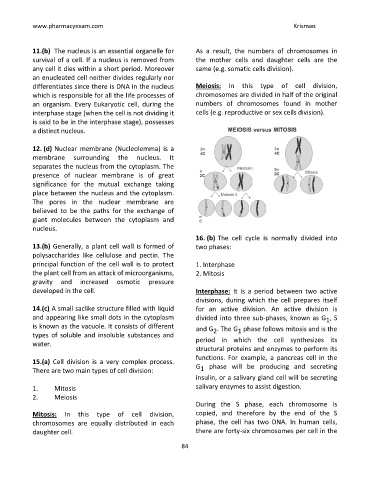
11.(b) The nucleus is an essential organelle for As a result, the numbers of chromosomes in
survival of a cell. If a nucleus is removed from the mother cells and daughter cells are the
any cell it dies within a short period. Moreover same (e.g. somatic cells division).
an enucleated cell neither divides regularly nor
differentiates since there is DNA in the nucleus Meiosis: In this type of cell division,
which is responsible for all the life processes of chromosomes are divided in half of the original
an organism. Every Eukaryotic cell, during the numbers of chromosomes found in mother
interphase stage (when the cell is not dividing it cells (e.g. reproductive or sex cells division).
is said to be in the interphase stage), possesses
a distinct nucleus.
12. (d) Nuclear membrane (Nucleolemma) is a
membrane surrounding the nucleus. It
separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm. The
presence of nuclear membrane is of great
significance for the mutual exchange taking
place between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
The pores in the nuclear membrane are
believed to be the paths for the exchange of
giant molecules between the cytoplasm and
nucleus.
16. (b) The cell cycle is normally divided into
13.(b) Generally, a plant cell wall is formed of two phases:
polysaccharides like cellulose and pectin. The
principal function of the cell wall is to protect 1. Interphase
the plant cell from an attack of microorganisms, 2. Mitosis
gravity and increased osmotic pressure
developed in the cell. Interphase: It is a period between two active
divisions, during which the cell prepares itself
14.(c) A small saclike structure filled with liquid for an active division. An active division is
and appearing like small dots in the cytoplasm divided into three sub-phases, known as G , S
1
is known as the vacuole. It consists of different and G . The G phase follows mitosis and is the
types of soluble and insoluble substances and 2 1
water. period in which the cell synthesizes its
structural proteins and enzymes to perform its
functions. For example, a pancreas cell in the
15.(a) Cell division is a very complex process.
1
There are two main types of cell division: G phase will be producing and secreting
insulin, or a salivary gland cell will be secreting
1. Mitosis salivary enzymes to assist digestion.
2. Meiosis
During the S phase, each chromosome is
Mitosis: In this type of cell division, copied, and therefore by the end of the S
chromosomes are equally distributed in each phase, the cell has two DNA. In human cells,
daughter cell. there are forty-six chromosomes per cell in the
84